Rabbit SingleB® mAb Discovery Service
Due to its unique ontogenetic mechanism, rabbits generate antibodies that combine high affinity with high specificity, precise recognition and excellent stability, overcoming application limitations seen in plenty of applications with antibodies generated with other host species, including IHCs, clinical diagnosis and therapeutic antibody development. For example, the affinity level of rabbit antibodies can reach picomolar level, providing super high sensitivity for clinical diagnosis and treatment, therefore reducing drug dose and broadening therapeutic window. In addition, their excellent ability of recognizing small size substances and fine epitopes makes rabbit antibodies the most favorable choice in the development of immunodiagnostic reagents and antibody drugs.
DetaiBio provides fast rabbit monoclonal antibody discovery service to help advance your rabbit antibody-based research. In contrast to resorting to rabbit hybridoma technology, scientist team in DetaiBio has built up Rabbit SingleB® mAb Discovery platform based on our unparalleled expertise in single B cell screening. With this powerful solution, rabbit antigen-specific memory B cells and plasma cells are directly screened in a single-cell level for antibody information. Amazingly, it only takes as short as 49 days from animal immunization to obtaining at least 50 unique, high-quality, FACS-validated antibody molecules for downstream evaluations.
Service Features
Highly Efficient
whole process lasts for 1.5 months
100 days less than hybridoma
No Commercialization Restrictions
Direct screening of B cells
No hybridoma commercialization restrictions
“1+1” Double Guarantee
PBC&MBC
double screening, double guarantee
High Probability
High antibody diversity
Higher probability of discovery of unique epitopes
Procedure
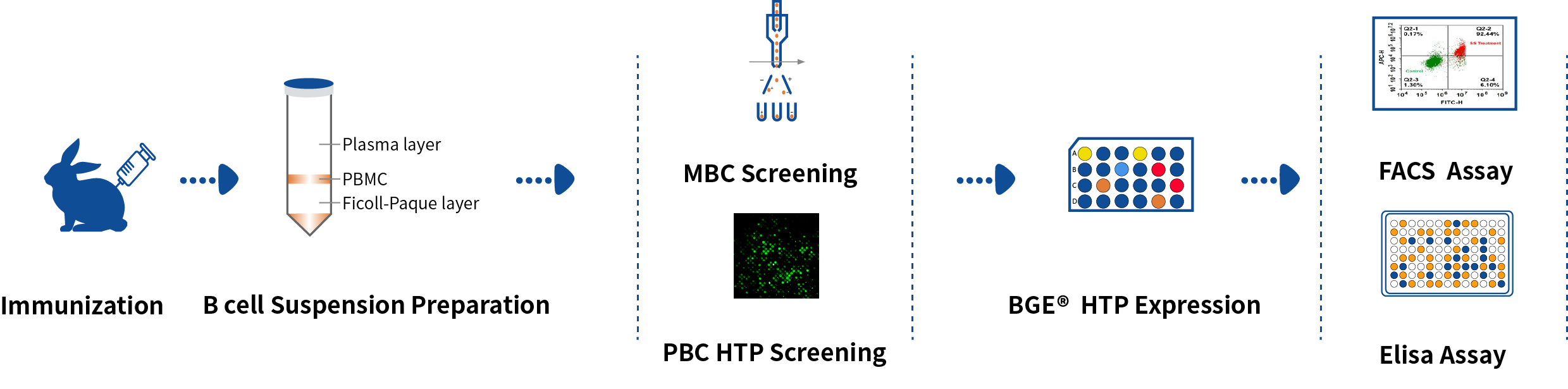
Workflow
| Stage | Service | Timeline | Deliverables |
|---|
| Stage Ⅰ Animal Immunization | - Antigen preparation (optional)
- Animal immunization
- Serum titer test
| 48 days | Premium Package- FACS binders >50
- Ensure sequence diversity
- Antibody sequence and expression plasmid
- CoA
Economic Package - 10 ELISA positive clones
- Antibody sequence and expression plasmid
- Select one strain purified 1 mg antibody
- CoA
|
| Stage Ⅱ “1+1”Double Screening | - MBC screening
- PBC screening
|
| Stage Ⅲ BGE® HTP Expression & Functional Test | |
| Stage Ⅳ Monoclonal Antibody Gene Sequencing | |
| Stage Ⅴ Expression and Purification of Recombinant Antibody (optional) | - Transfection level plasmid preparation
- Transient transfection expression
- HTP purification
- Endotoxin control
| For enquiry |
Advantages of SingleB®
| DetaiBio SingleB® | Homologous Hybridoma | Heterologous Hybridoma | Phage Library |
|---|
| Limitation | High technical threshold | Rabbit hybridoma commercialization restrictions | Poor stability of heterologous fusion | Depending on the correct transcription, translation, folding and assembly of light chains in bacteria |
| Source of Antibody | MBC & PBC | PBC | PBC | MBC & PBC |
| Heavy & Light Chain Pairing | Natural pairing | Natural pairing | Pairing Damage | Unnatural pairing |
| Throughput x Diversity | High | Low | Low | Medium |
| Timeline | 48 days | 5-6 months | 3-4 months | 3-4 months |
| Price | Low | Low | Medium | High |
| Deliverables | Full length antibody sequence & Recombinant plasmid | Hybridoma (easy to degenerate) | Antibody sequence | scFv、Fab、VHH sequence & Recombinant plasmid |
Case Study
Rapid Immunization of Rabbits
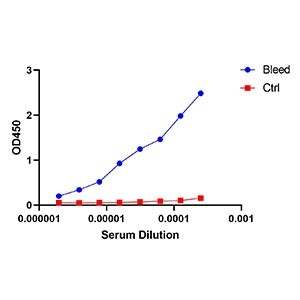
DetaiBio self-developed immunization method with serum titer greater than 1:100K.
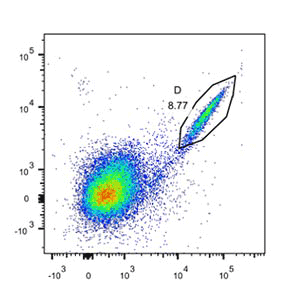
Specific memory B cells were screened by cell surface marker and antigen.
Antibody Functional Verification
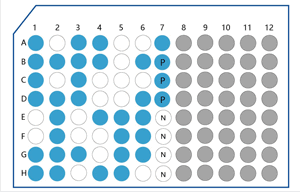
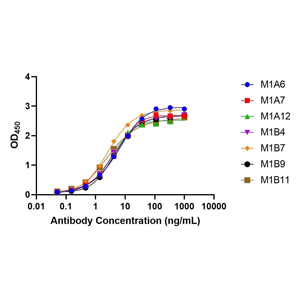
The antibody supernatant was obtained by amplification and HTP expression. ELISA was performed on the supernatants and 31 positive clones were found, with a positive rate of 63.3%.
Antibody Affinity Verification
Rabbit monoclonal antibodies discovered by SingleB® Fast mAb discovery platform shows high affinity.
Advantages of Rabbit mAb
- Stable Structure: 90-95% of light chains are κ1, κ1 makes the light chain structure more stable.
- High Affinity: The Kd value of antibody is 10-12M, and its affinity is 100-1000 times that of conventional antibody.
- Accurate recognition: It recognizes small molecules (< 600 Da), PTM, single amino acid substitution and other subtle epitope changes.
- Rich Diversity: The non inbred lines propagate, with long affinity maturation time, and the diversity mechanisms of sGC and SHM are combined.
- Strong Immune Response: it can produce strong immune response to small molecule antigen and hapten.
Unique Antibody Structure
Rabbit IgG has no subclasses, and there are fewer amino acids in the N-terminal and D-E ring, which is easy for molecular cloning and engineering design, and is more suitable for antibody drug development. Rabbit anti 90-95% of light chains are κ 1. There is an in chain disulfide bond between VL and Cl, and the light chain structure is more stable. Rabbit monoclonal antibodies can recognize small molecules, post-translational modifications, single amino acid substitution and other subtle epitope changes, and the specificity of epitope recognition is higher.
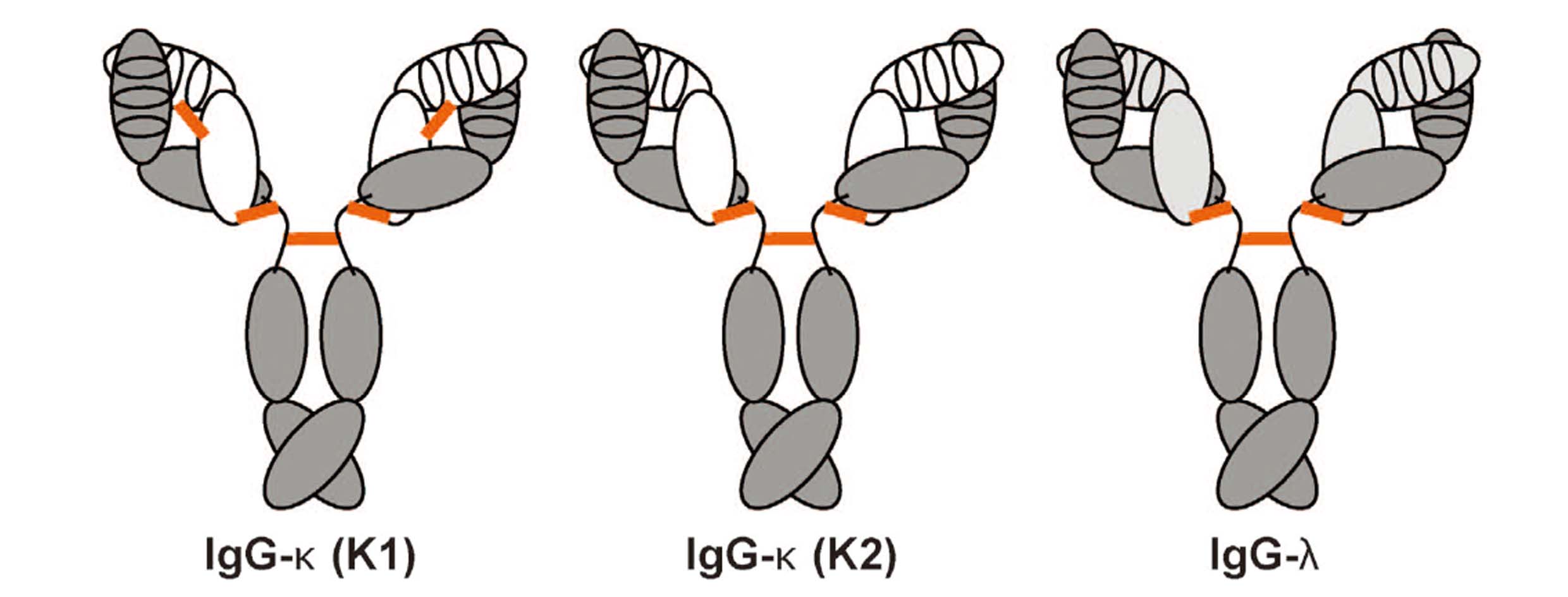
Fig1. Schematic diagram of natural rabbit IgG
Note: White part represents light chainκ; Light grey part represents light chain λ; Dark gerypart represents heavy chain; Orange part represents disulfide bond
Unique B Cell Development Mechanism
Rabbits produce antibody libraries through different immune mechanisms from mice and humans, which can produce a strong immune response to foreign antigens, and are also applicable to small molecules and haptens with weak immunogenicity. Human and mice create an anti library through VJ and VDJ gene rearrangement, and then further diversify through somatic hypermutation (SHM). In addition to the SHM mechanism, rabbits can also introduce additional antibody diversity through somatic gene conversion (SGC).
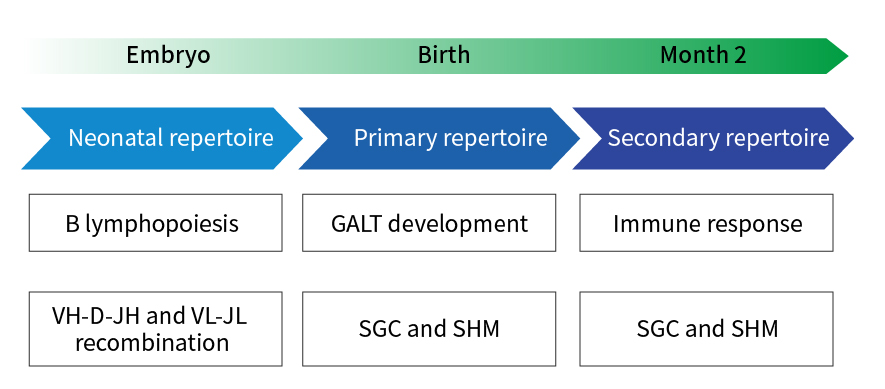
Fig2. Rabbit B cells and antibody library development
Note: GALT: gut-associated lymphoid tissue
Related Service