TCR Targeted Tumor Antigens:
Prime Candidates for Cancer Immunotherapies
TCR-targeted cancer antigens, due to their high disease-specificity, have gained increased attention in recent years, especially in the treatment of solid tumors for which there has been a severe lack of “clean” targets for improved efficacy and safety profiles in clinical studies and practices.
A typical TCR structure of CD8+ T cells is illustrated as below.
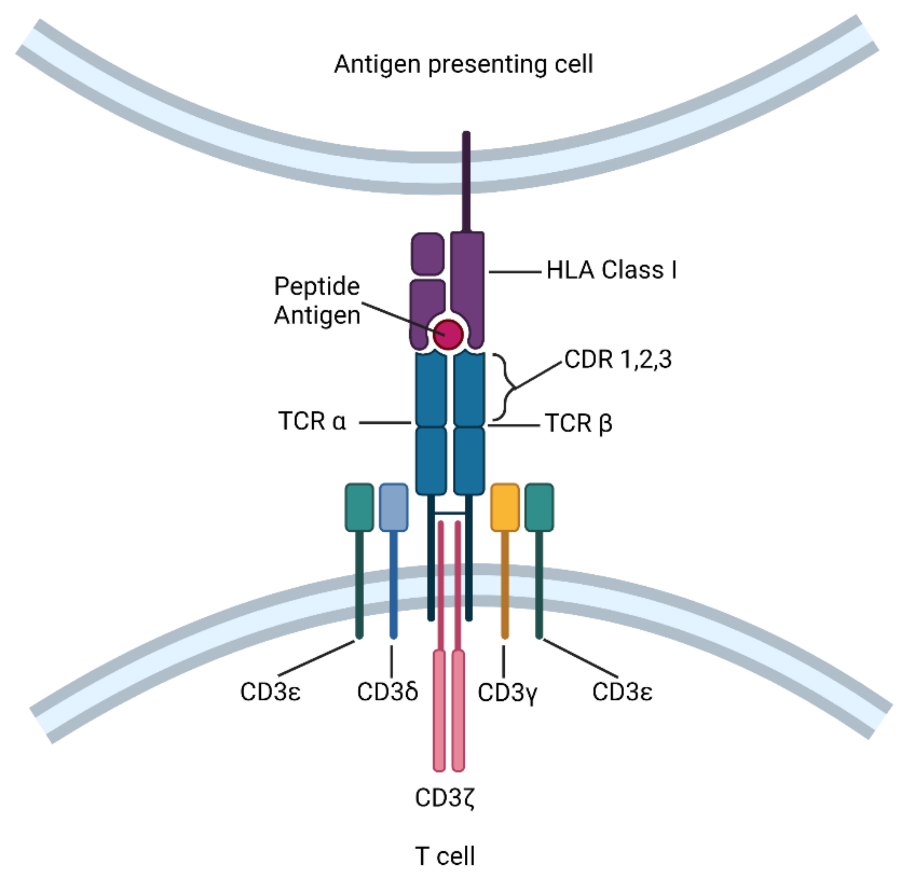
In recently years, significant progress has been achieved in identifying the precise and presentable cancer antigens, some of which, excitingly, have been clinically tested for mediating immune rejection of disease cells, as briefly summarized as follows.
1. Tumor-associated antigens (TAAs): they are, generally, expressed by tumor cells but also in some healthy tissues, potentially leading to on-target off-tumor toxicity. Among them are:
- 1) Differentiation antigens: expressed by cancer cells as well as normal cells of the same tissue origin, such as GP100; clinically appropriate to target when their expression is restricted to dispensable healthy tissues.
In early 2022, FDA approved KIMMTRAK by Immunocore, a TCR/ CD3 bispecific fusion protein for uveal melanoma treatment, targets presented GP100.2 Besides, KIMMTRAK is the first T cell engager drug ever approved for solid tumor treatment. This new class of T cell–redirecting bispecific fusion proteins, as illustrate below , use an engineered high-affinity TCR to target intracellular antigens presented as a peptide–HLA complex on target-cell surface. 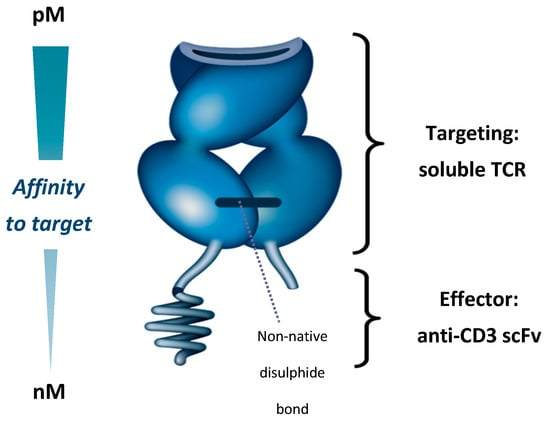
- 2) Overexpressed antigens: expressed at high levels in cancer cells but minimally expressed in healthy cells; the differential expression makes possible a therapeutic window.
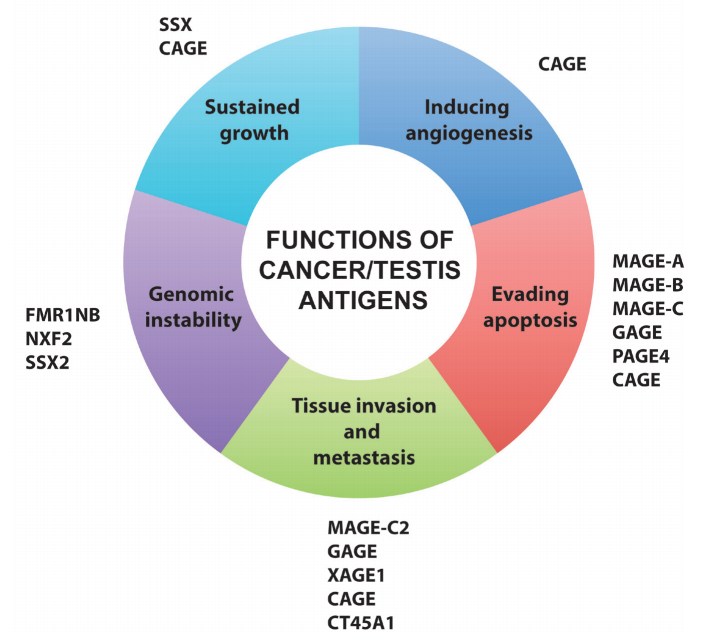
- 3) Cancer-germline antigens (CGAs): expressed in immune-privileged germline tissues (which lack antigen presentation machinery), while epigenetically silenced in somatic tissues; becoming aberrantly re-expressed in tumors to promote oncogenesis, thus greatly reducing the risk for on-target off-tumor toxicity. CGAs are being identified, as indicated below , and some of them have been investigated for cancer treatment studies.3
2. Tumor-specific antigens (TSAs): they are genetically encoded in cancer cells but not present in the genome of any normal cells, allowing for excellent therapeutic window.
1) Viral antigens: identified in viral oncogene driven cancers; but nearly absent in normal cells.
Ebvalla developed by Atara., a first ever allogeneic (off-the-shelf) T-cell therapy approved by EU indicated for a rare but deadly lymphoma, targets presented Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) viral oncoproteins
Although not a TCR therapy, its approval clinically validates the therapeutic values of viral antigens.
- 2) Neoantigens: expressed exclusively by cancer cells due to their genomic instability; attractive targets that would pose essentially no risk for on-target off-tumor toxicity.
While most neoantigens are ineffective, public neoantigens from driver mutations expressed homogenously and shared among patients are immunogenic and restricted to a common HLA.
KRAS G12V is an optimal example. AFNT-211, a TCR-T cell therapy targeting KRAS G12V-expressing solid tumors, is to enter clinical trial.
More breakthroughs are expected from cancer antigen-targeted TCR therapies.
Precision makes efficacy and safety.
DetaiBio is leveraging its single T cell sorting platform and single cell RT-PCR technology to unlock its TCR discovery-based therapy research. Please contact us for potential collaboration.
Reference
1. Sun, Y., Li, F., Sonnemann, H., Jackson, K. R., Talukder, A. H., Katailiha, A. S., & Lizee, G. (2021). Evolution of CD8+ T cell receptor (TCR) engineered therapies for the treatment of cancer. Cells, 10(9), 2379.
2. Gjerstorff, M. F., Andersen, M. H., & Ditzel, H. J. (2015). Oncogenic cancer/testis antigens: prime candidates for immunotherapy. Oncotarget, 6(18), 15772.
3. Hoffmann, M. M., Brown, L., Campbell, M., Pechhold, K., Brate, A., He, X., ... & Schmitt, T. M. (2023). AFNT-211: A FAS-41BB–enhanced TCR-T cell therapy with stem-like properties targeting KRAS G12V-expressing solid tumors. Cytokine, 1, 1-50.
Welcome to the Discovery on Target, from DetaiBio!
Discovery on Target 2023 will be held in Sheraton Boston, Boston, MA from September 25-28, 2023. DOT covers breakthroughs in current and emerging "hot" targets and technologies, as well as target validation methodologies for the discovery and development of innovative therapeutic treatments ranging from biologics to small compounds. During the congress, experts and scholars can visit multiple concurrent sessions for insightful lectures, vigorous debate, and important interactions with colleagues.

Conference Informantion
Conference Name: Discovery on Target 2023
Conference Time: September 25-28, 2023
Conference Venue: Sheraton Boston, Boston, MA
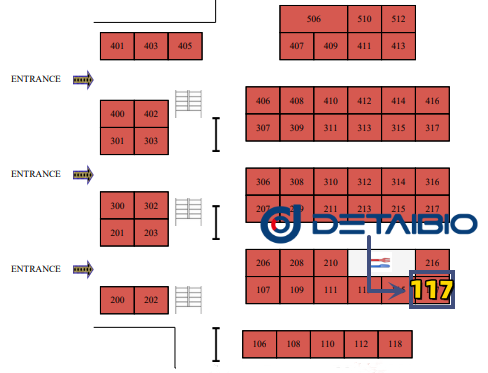
DetaiBio Booth: #117
Conference Agenda (partial listed)

Whole List: https://www.discoveryontarget.com/programs
About Us
Detai Bioscience, Inc. (“DetaiBio”), is a CRO vendor focusing on antibody discovery and functional protein research field. DetaiBio is aiming to provide high quality and economic service to speed up life science for our clients in different fields, such as antibody drug discovery, in-vitro diagnosis and academic research.
The main services offer by DetaiBio:
——SingleB® for antibody/VHH discovery service
——High-throughput recombinant antibody expression service (2 week delivery)
——Hybridoma sequencing service
——Customized protein expression service ( E.coli, Mammalian)
Follow Us
Captivating Mechanism of Action behind Monoclonal Antibodies
Based on this structural feature of mabs, we can roughly divide their mechanisms of action into Fab-related and Fc-related mechanisms of action.
Action of Fab
As the antigens recognized by monoclonal antibodies have different physiological functions, the corresponding antibodies also have different functions, including neutralization of free protein target molecules and antagonism or activation of cell surface receptors.
1.Recognize Free Molecular Targets
Cytokines, growth factors, biotoxins and viruses that exist free in the blood circulation can be used as the targets of monoclonal antibodies. Protein factors regulate the function of cells by binding to receptors and transmitting signals into cells. The mechanism of action of neutralizing antibodies is to neutralize the antigen by binding to the antigen, so that the antigen loses the ability to bind to the receptor, and then loses its biological function.
Examples: Bevacizumab, Infliximab, Adalimumab, Raxibacumab
2.Recognize Cell-surface Receptors
Each antibody can specifically bind to a specific antigenic target. The target antigen is expressed on a specific cell surface and has a specific function, such as cell activation, growth, or migration. According to the Fab activity of the antibody, the interaction between the antibody and its target receptor can be divided into binding, antagonism, and activation. Most of the targets that are recognized and bound by antibodies are tumor-associated antigens, which are growth factor receptors that are overexpressed by many malignant tumors. Either antibody inhibits cell growth, induces apoptosis, and arrests the cell cycle by binding to its receptor, affecting its function, and interfering with signal transduction.
Examples: Cetuximab, Panitumumab, Trastuzumab, Rituximab
Action of Fc
The Fc region of a monoclonal antibody determines the effector functions of the antibody, including antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC). ADCC is triggered by FC interaction with FyRIa while CDC is triggered by Fc interaction with a range of complement system components in blood.
1.Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC)
When the antibody binds to the surface antigen of tumor cells through the antigen-binding site, and the Fc site binds to the Fc receptor on the surface of immune effector cells, the immune effector cells are activated and kill the tumor target cells. This process is called ADCC. The strength of ADCC mediated by monoclonal antibodies is related to many factors. In general, the closer the binding between tumor target cells and immune effector cells through antibody bridging, the stronger the ADCC effect.
2.Complement-dependent Cytotoxicity (CDC)
Different types of antibodies has different ability to inspire the CDC. Complement is a group of heat-labile, enzymically active proteins present in the serum and tissue fluids of humans or vertebrates. The main function of the complement system is to damage the cell membrane or regulate the surface of pathogens for macrophages to swallow by acting on the surface of pathogens and other targets. In addition, it can also cause inflammatory responses.
Acquired immune response
In addition to directly interfering with the biological functions of antigens by binding to target antigens and mediating immune responses such as ADCC and CDC through Fc fragments, monoclonal antibodies can also cause adaptive immune responses. It includes cellular immunity such as the activation of tumor antigen-specific cytotoxic T cells and helper T cells, and humoral immunity such as the production of protective antibodies against tumor antigens.
Materials
Antibody Affinity Maturation
Antibody affinity maturation refers to a state of normal immune function. In humoral immunity, the average affinity of antibodies produced in a second response is higher than that of the initial immune response. This phenomenon is called antibody affinity maturation.
This functional state of the body is the result of long-term evolution and continuous adaptation to the external environment and is of great importance for the body's defense and maintenance of autoimmune surveillance.
In Vivo Affinity Maturation
Antibody affinity maturation is formed as a result of genetic mutations in the antibody-forming cells themselves and selective activation of B-cell clones by antigen. After the body receives antigenic stimulation, somatic cells undergo high-frequency mutations, and the mutations produce various B-cell clones with different affinities, which are captured by follicular dendritic cells, resulting in an increase in the average affinity of the progeny B cells, thus achieving in vivo maturation of the affinity.
In the body's humoral immune system, B lymphocytes are induced to produce antibodies in response to antigen stimulation. During repeated exposure to antigen, antibodies with high affinity are produced. This process involves two interrelated processes. First, random rearrangement of the light and heavy chain germline gene fragments of the bone marrow antibody by V-(D)-J to produce more than 106 combinations is the molecular basis of the antibody specific immune response. Second, after antigen stimulation, antibody genes, especially the complementarity determining region (CDR), undergo frequent mutations in the germinal center of secondary lymphoid organs, which lead to changes in antibody binding properties. The filtered dendritic cells present the antigen, and only the B cells with the highest antigen affinity will choose survival for further differentiation into plasma cells and memory cells.
In Vitro Antibody Affinity Maturation
The development of antibody preparation technology has gone through 3 stages of development: polyclonal technology, monoclonal technology and antibody library technology. Compared with mono- and polyclonal techniques, antibody library technology is very flexible at the gene level, and can analyze, modify and process gene sequences to improve antibody properties or give antibodies new properties, breaking through the previous limitations limited to the design of anti-antigen molecules. However, practical applications of antibody library-derived antibodies are very rare compared to traditional monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies, mainly because library-derived antibodies have low affinity compared to natural antibodies, making it difficult to meet a variety of practical needs. In particular, the affinity of antibodies from unimmunized natural antibody libraries is usually at the micromolar level, which is only comparable to the affinity level of antibodies obtained by animals after the initial immune response. Therefore, in vitro affinity maturation studies have been conducted based on the principle of in vivo antibody affinity maturation, simulating the in vivo affinity maturation process and adopting various strategies to mutate antibody genes accordingly.
Commonly Used In Vitro Affinity Maturation Techniques for Antibodies
According to the principle of in vivo antibody affinity maturation, the selection of mutation regions and how to introduce mutations during in vitro antibody affinity maturation is a key issue, and the current mutation strategies are divided into three main categories, random mutations, substitutions and targeted mutations.
Error-prone PCR
Error-prone PCR is currently the most commonly used antibody mutagenesis technique, which can introduce random mutations in the full length or part of the antibody gene. During amplification of the target gene by polymerase, mutations are randomly introduced into the target gene at a certain frequency by applying a polymerase with a high mismatch rate or adjusting the reaction conditions, etc. Random mutations are repeatedly induced by multiple rounds of PCR to accumulate mutation effects and finally obtain random mutants of the target protein.
Strand Displacement
Strand displacement is the combination of retaining the heavy or light chain of a specific antibody and combining the other chain with a randomized complementary chain, from which a more active mutant strain is screened. By fixing one of the two chains of an antibody and constructing a replacement library with sufficient diversity for the other chain, the randomized combination has the potential to produce the best chain combination, which can be screened by phage antibody libraries to obtain new high-affinity antibodies. Strand displacement strategies often employ light chain substitutions.
Site-directed Mutagenesis
Since natural antibodies are not uniformly distributed in the region where high-frequency mutations occur in somatic cells during affinity maturation, they are mainly concentrated in the CDR region that is in direct contact with the antigen. The CDR region is the most commonly selected region for targeted mutagenesis during the affinity maturation of antibodies in vitro, so that sufficient sequence diversity can be obtained without disrupting the protein structure. When performing fixed-point mutagenesis on CDRs, multiple CDRs can be mutated in parallel or optimized stepwise.
DNA Shuffling
DNA shuffling is a technique in which homologous antibody genes are cleaved into fragments of no more than 50bp using deoxyribonuclease I, then randomly combined and amplified into completed antibody genes by PCR. It contains the process of randomized cleavage, recombination and screening of antibody fragments, which to some extent mimics the affinity maturation process of natural antibodies and accelerates the rate of in vitro directed evolution.
Q&A
1. Why are light chains usually replaced in strand displacement?
Because the heavy chain of antibody is more important in terms of antibinding activity and structure, so the strand displacement strategy often uses light chain replacement to avoid changes in antibody binding specificity after strand displacement as much as possible.
2. What are the advantages and disadvantages of antibody library technology compared with mono- and polyclonal antibody technology?
Advantages: large screening range of antibody library, short experimental cycle, simple operation, no immunization operation, can be applied to mass production
Disadvantages: weak affinity, not easy to stimulate the human antigen-antibody reaction; clinical application is limited.
Join DetaiBio at the Next-Gen Immuno-Oncology Conference!
The 6th Annual MarketsandMarkets Next Gen Immuno-Oncology Conference, which will be held on the 22nd and 23rd of June 2023 at the Hilton Boston Logan Airport in Boston, will cover the difficulties and future directions in IO research. The congress seeks to bring together academicians, researchers, and scientists from research institutes, pharmaceutical, bio-pharmaceutical, and biotechnology firms to discuss the most recent developments in ADC, Bispecific Antibodies, Cellular Therapy, and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors development.
This congress would also include diverse combination techniques, pre-clinical and translational immune-oncology advances, cellular and viral therapy updates, vaccine development, and customized immunotherapy. Keynote speeches, Brainstorming Panel Discussions, and Case Studies will allow stakeholders to discuss and comprehend the issues at hand, as well as come up with solutions. With over 20 presenters from pharma, bio-pharma, and biotech businesses from across the world, the congress will cover the most recent developments in the development of ADCs, Monoclonal Antibodies, Bispecific Antibodies, Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors, and Cellular Therapy.

Conference Informantion
Conference Name: Next-Gen Immuno-Oncology Conference
Conference Time: June 22-23, 2023
Conference Venue: Hilton Boston Logan Airport, Boston
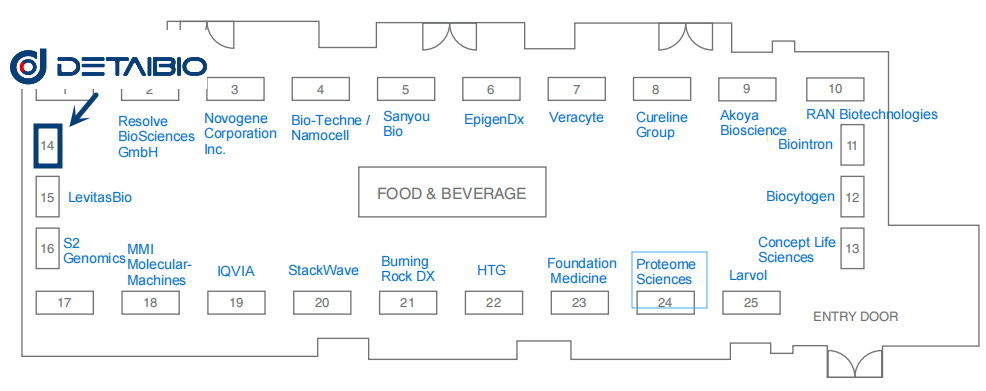
DetaiBio Booth: #14
Conference Agenda (partial listed)
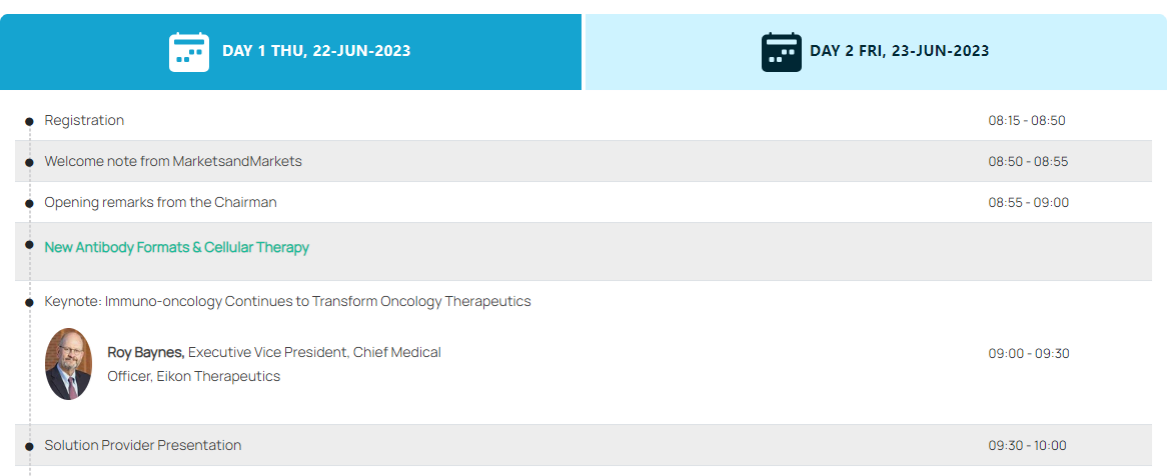

Whole List: https://events.marketsandmarkets.com/6th-annual-immuno-oncology-conference-boston/
About Us
Detai Bioscience, Inc. (“DetaiBio”), is a CRO vendor focusing on antibody discovery and functional protein research field. DetaiBio is aiming to provide high quality and economic offer service to speed up life science for our client in different fields, such as antibody drug discovery, in-vitro diagnosis and academic research.
The main services offer by DetaiBio:
——SingleB® for antibody/VHH discovery service
——High-throughput recombinant antibody expression service (2 week delivery)
——Hybridoma sequencing service
——Customized protein expression service ( E.coli, Mammalian)
Follow Us
Join the BIO International Convention 2023 with DetaiBio!
The BIO International Convention will be held June 5-8 at the Boston Convention & Exhibition Center in Boston. The BIO International Convention draws 14,000+ biotechnology and pharmaceutical leaders for one week of rigorous networking to uncover new prospects and intriguing partnerships, with over 400 exhibitors. The conference is programmed around current and future innovations in biotechnology, including areas such as the therapeutic frontier, biotechnology business, and regulatory and policy outlooks.

Conference Informantion
Conference Name: BIO International Convention
Conference Time: June 5-8, 2023
Conference Venue: Boston Convention and Exhibition Center, 415 Summer St, Boston, MA, 02210
DetaiBio Booth: #3568
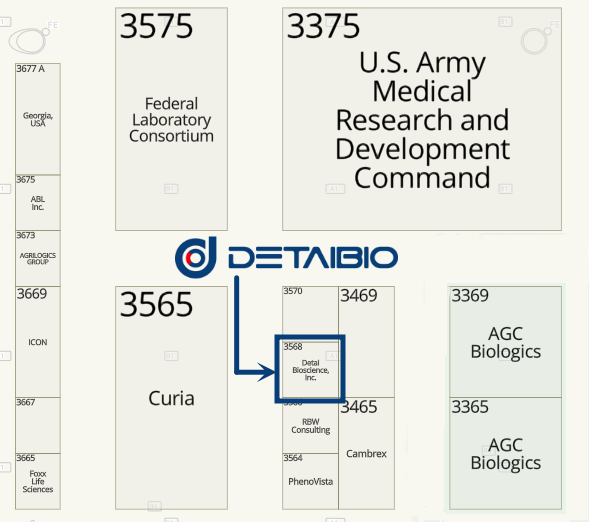
Conference Agenda (partial listed)

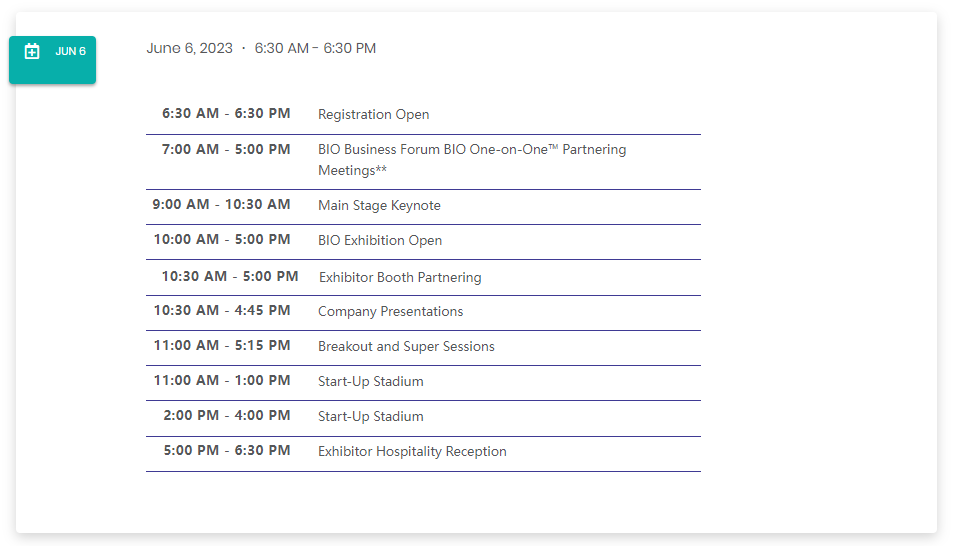
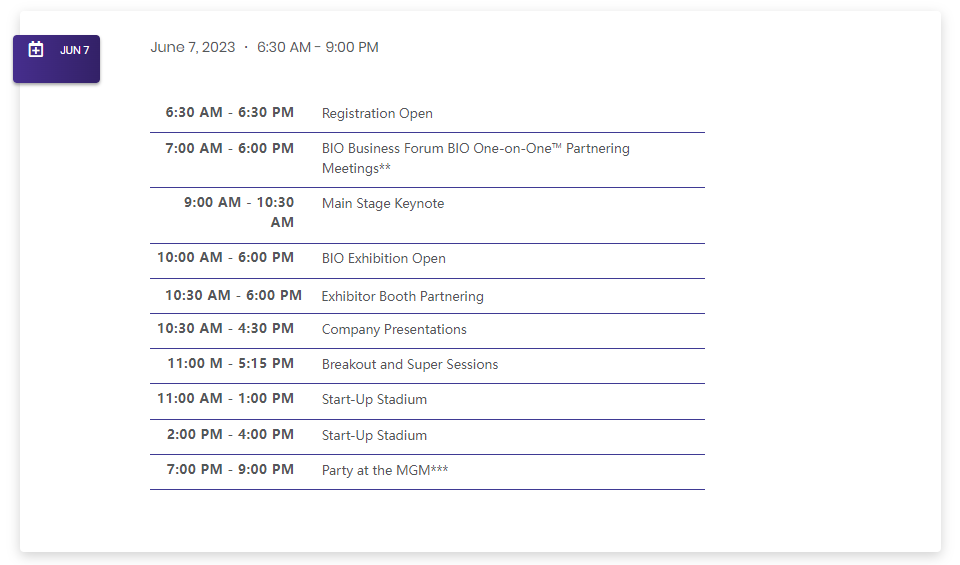

Whole List: https://www.bio.org/events/bio-international-convention/schedule
About Us
Detai Bioscience, Inc. (“DetaiBio”), is a CRO vendor focusing on antibody discovery and functional protein research field. DetaiBio is aiming to provide high quality and economic offer service to speed up life science for our client in different fields, such as antibody drug discovery, in-vitro diagnosis and academic research.
The main services offer by DetaiBio:
——SingleB® for antibody/VHH discovery service
——High-throughput recombinant antibody expression service (2 week delivery)
——Hybridoma sequencing service
——Customized protein expression service ( E.coli, Mammalian)
Follow Us
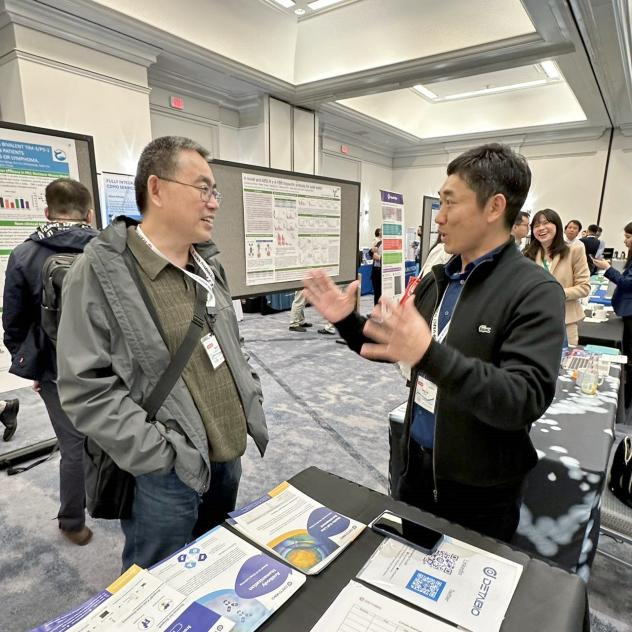
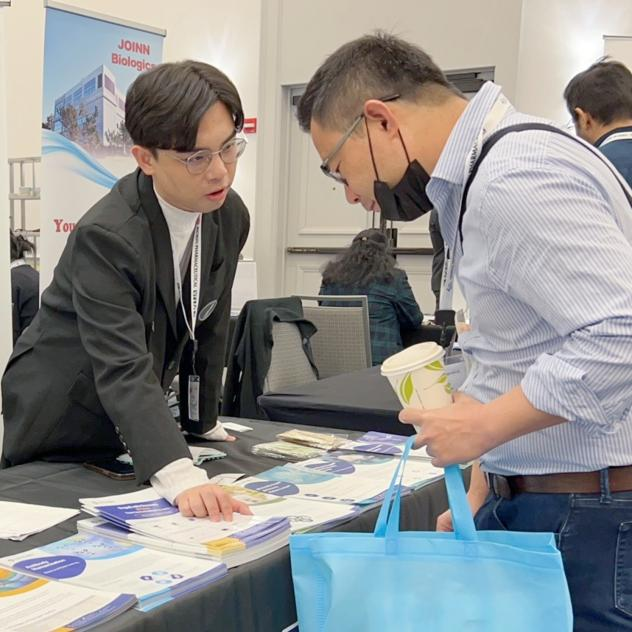
Exhibition review | 2023 Chinese Antibody Annual Conference ended successfully
On May 14, 2023, the Chinese Antibody Society (CAS) successfully held its annual meeting in Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA. The theme was "Post COVID-19 Pandemic: New Frontiers and Opportunities of Antibody-based Biologics". This annual meeting brought together professional scholars, experts and enterprise representatives from all over the world to conduct in-depth discussions and exchanges on cutting-edge technology and research results related to antibodies.

During the exhibition, DetaiBio attracted the attention of many industry people with SingleB® antibody discovery platform. The technical team led by Dr. Gang Liu shared the procedure, service features and case studies of SingleB® antibody discovery platform.
The SingleB® antibody discovery platform independently developed by DetaiBio is suitable for multiple animal species such as mice, rabbits, alpacas and so on, with high antibody discovery efficiency and high throughput. To obtain as many antibodies as possible, we used two different platforms, the SmartFlow® FACS platform for memory B cells screening and the DeepLight® platform for plasma cells screening. In addition, our self-developed single B-cell PCR kit can perform single cell sequencing. Therefore, antibodies obtained by the SingleB® antibody discovery platform are naturally mature in vivo and have rich genetic diversity, which can provide more candidate antibody molecules for antibody drug development.
About Us
Detai Bioscience, Inc. (“DetaiBio”), is a CRO vendor focusing on antibody discovery and functional protein research field. DetaiBio is aiming to provide high quality and economic offer service to speed up life science for our client in different fields, such as antibody drug discovery, in-vitro diagnosis and academic research.
The main services offer by DetaiBio:
——SingleB® for antibody/VHH discovery service
——High-throughput recombinant antibody expression service (2 week delivery)
——Hybridoma sequencing service
——Customized protein expression service ( E.coli, Mammalian)
Follow Us